Analysis and reporting
Analysis and reporting is a central component of energy management in modern buildings. Through systematic data collection, analysis and evaluation, operators can maximize the efficiency of their technical building systems, reduce costs and ensure sustainable operation.
1. Data acquisition
Sensors and measuring devices
- Energy consumption measurement: Sensors continuously record the energy consumption of heating, ventilation, air conditioning (HVAC), lighting and other systems.
- Ambient conditions: Sensors measure temperature, humidity, CO2 content and light intensity to ensure an optimum indoor climate.
- Performance parameters: Additional sensors monitor current voltage, strength and frequency as well as water and gas flows.
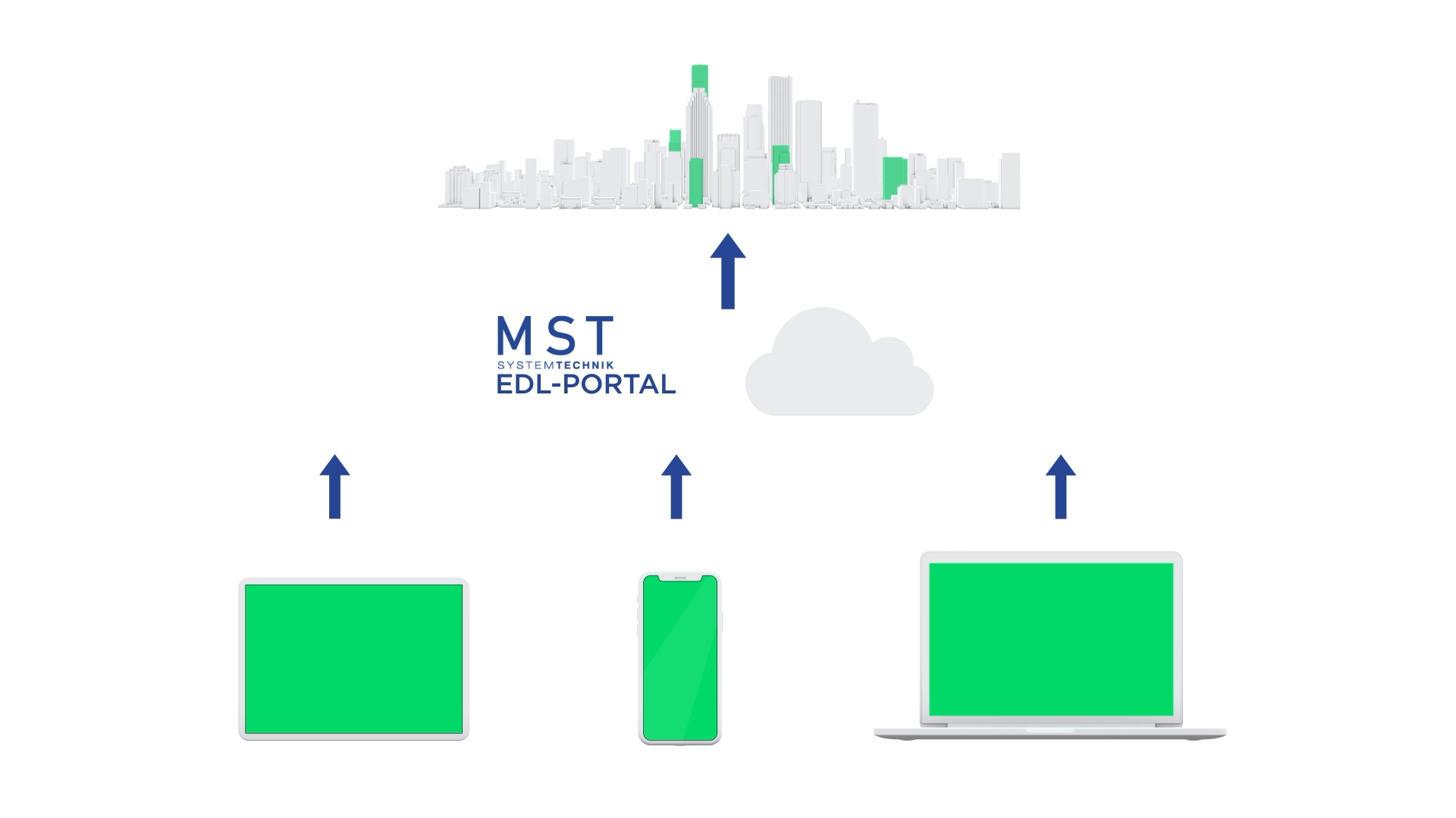
Data transmission
- The collected data is transferred in real time to central databases or cloud platforms that are integrated into the EDL portal.
2. Data analysis
Real-time analysis
- Dashboards and visualizations: Interactive dashboards provide a visual representation of real-time data, enabling immediate insight into energy consumption and identifying trends and anomalies.
- Anomaly detection: Automated systems detect deviations from normal operating parameters and report irregularities immediately.
Historical data analysis
- Comparative analysis: Historical data is analyzed to compare current energy consumption with previous periods. This analysis helps to identify long-term trends and patterns.
- Performance evaluation: By evaluating performance over a longer period of time, operators can determine which energy-saving measures have been successful and which have not.
Predictive analysis
- Prediction models: Machine learning algorithms are used to create prediction models that predict future energy consumption based on historical data and current operating conditions. prognostizieren.
- Maintenance planning: Predictive analyses help to plan upcoming maintenance work by predicting when components are likely to fail.
3. Reporting
Regular reports
- Standard reports: Automatically generated standard reports provide a regular overview of energy consumption and operating efficiency. These reports can be generated daily, weekly, monthly or annually.
- Customizable reports: Operators can request specific reports tailored to their individual needs, e.g. reports on the energy consumption of individual systems or departments.
Detailed analyses
- Cost analysis: Reports include detailed cost analyses that show the financial impact of energy consumption and identify opportunities to reduce costs.
- Benchmarking: Reports compare the building's performance with similar facilities to identify efficiency potential.
Alarm and fault reports
- Event logs: These reports document all faults and alarms that have occurred, including the root cause analysis and the measures taken.
- Performance reports: They show the response times and the effectiveness of troubleshooting.
Certification support
- Sustainability reports: These reports document the measures taken to improve energy efficiency and support compliance with sustainability standards and certifications such as DGNB, LEED or BREEAM.
- Compliance reports: They ensure compliance with legal regulations and standards in the area of energy management.
4. Benefits of analysis and reporting
Cost savings
- By precisely analyzing and optimizing energy consumption, considerable cost savings can be achieved.
- Identifying and eliminating inefficient operating practices helps to reduce operating costs.
Energy efficiency
- Continuous monitoring and optimization of energy consumption leads to a significant improvement in energy efficiency.
- Sustainable practices and technologies are promoted and integrated.
Transparency and control
- Operators receive full transparency about the energy consumption and operating conditions of their systems.
- The ability to make well-founded decisions is significantly improved by detailed reports and analyses.
Improved operational management
- The identification of weak points and optimization opportunities leads to better operational management.
- Continuous performance monitoring enables proactive maintenance planning and reduces downtime.
Support for certifications
- Detailed reports support the certification process and help to meet the required standards and specifications.
- The documentation of energy efficiency measures is crucial for obtaining environmental certificates.
Conclusion
Analysis and reporting as part of the monitoring and control of technical building systems offers numerous benefits for operators and owners. By using state-of-the-art technologies and integrated systems, energy consumption and operating efficiency can be optimized, costs reduced and sustainability goals achieved. With the support of the EDL portal, these processes can be efficiently implemented and continuously improved.